The basic process for succeeding with your SEO is as follows:
-
Perform initial keyword research
-
Align your website to keyword topics
-
Optimise your website pages thoroughly
-
Create supporting content and optimise for keywords
-
Monitor, adapt and improve performance over time.
Step 1 - Perform initial keyword research
Before doing any optimisation, you need to perform keyword research to identify the most attractive keywords to optimise for.
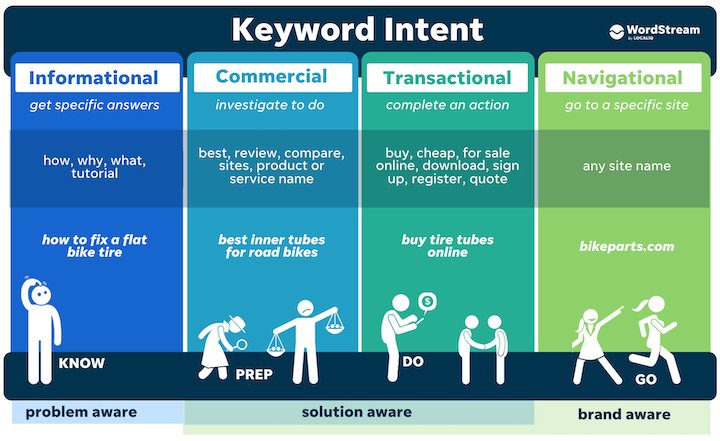
Keyword research is the process of using tools to identify keywords that:
- Are highly relevant to your business
- Have good search volume
- Have reasonable difficulty
If a keyword meets all of these criteria, then it is attractive.
Not all of the keywords you find will meet all of these criteria though. In a B2B keyword strategy its ok to have a mixture of low search volume, high difficulty and attractive keywords - as long as they are all highly relevant.
In keyword research, everything is relative. None of the data you will be using is absolute. The goal is to do enough research that you end up with a set of keywords that are relatively better to target than many others.
In B2B marketing particularly, a lot of keyword strategy is just common sense - after all, you know what you do and you how your buyers describe it (see keywords vs buzzwords above). It is, however, invaluable as it can throw up interesting and unexpected results.
For example, terms that you thought should have high search volume may not, whereas close variants that you hadn't considered may have. We make these sorts of discoveries every day.
You may also find that terms you use frequently have another, more widely used, interpretation. This may mean that high search volumes are actually not relevant or attractive as the results are all on the other topic.
Once you have settled on a set of attractive keywords to form the basis of your evolving keyword strategy, you're ready to move on.
Step 2 - Building keywords into your sitemap
One of the strongest steps you can take towards better SEO and more organic search traffic is to build your sitemap around your keyword strategy.
This means creating pages that target specific keywords by including them in the URL and creating content around them.
Taking this approach results in website pages that are highly optimised for the terms your buyers actually use, and it guides your content creation strategy to capitalise on the opportunities created.
URLs are not only a ranking factor in themselves but keyword-optimised URLs help the user understand what you do, in their terms, increasing click-through rates.
Step 3 - Optimising your website pages for target keywords
Every page in your website should be optimised for different keywords. This is achieved by placing these keywords in the meta title, meta description, h1 title tag and, of course, the page content.
After you have selected which keywords you are optimising a page for, take the following steps.
Meta titles
Meta titles are one of the most important ranking factors in search engine algorithms. Secondly, the meta title is prominently displayed to the search user in search results.
The length of the titles shown in Google's search results are limited to about 55 characters and search engine algorithms place the most importance on words at the beginning of the title. So, short, focused titles are most effective.
Keywords in the page title are automatically bolded in Google's search result when they match the search query. This draws more attention and increases click through rate.
Therefore, the best approach to page titles is to use the target keywords alone, with nothing superfluous. Don't waste valuable space writing proper sentences, simply use keywords in order of importance, separated with simple punctuation marks like a pipe (|).
Leave out your company name, it just isn't needed. Including your company name wastes valuable characters and duplicates content that is contained in your URL.
Example: Keyword one | Keyword 2
Meta descriptions
Meta descriptions are not a ranking factor in themselves, so they do not influence where your page ranks for its target keywords. They are an in important SEO factor, however, as they can have a dramatic impact on how your pages appear in search results and how many users click through when seeing them.
When search engines show a result to a user, they show a snippet of text along with the page title. The search engine looks in the meta description and in the page for a passage of test that's contains the keywords in the user's search query. If your meta description contains the keyword, you can control what the search result looks like. If not, selection of the snippet is left to the search engine and the results are often less than desirable.
When writing your meta description, the aim is to build on the meta title and reassure the searcher that the page contains the information they are after.
To get the best results:
- Write your meta descriptions using proper sentences
- Feature your target keywords early on - they will be bolded if they feature in the search query
- Limit yourself to about 155 characters so that you write complete ideas that will be displayed in full most of the time
Be aware, search engines can still ignore your meta description and use a snippet of their own choosing - typically when your page is somehow seen in search results for keywords that the meta description isn't optimised for.
H1 title tag
H1 is the html tag applied to the most important, and usually biggest, title on a web page.
Search engines use the contents of the H1 tag as a ranking factor when deciding what your page is about. Multiple H1s on a page, or a H1 that is missing your target keyword will hamper SEO ranking.
Therefore, each page should only have one H1 title and it should contain the target keyword. Simple.
Step 4 - Creating content for long tail keywords
While optimising your main website for the most attractive keywords is of vital importance, it remains a fact that searches for long tail search terms vastly outnumber those for head terms.
Content marketing, particularly blogging, is the most efficient and effective way to target an increasing number of long tail terms over time.

By creating content for long tail search terms you can continually grow the organic search traffic to your site, building it to levels that you main site could not achieve alone.
In addition, the increasing search footprint that content marketing creates builds authority for your domain and, when content is optimised to support main website pages, will help your site to rank more highly for the competitive head terms in your keyword strategy.
Search engine optimisation differs slightly for content pages compared to main website pages.
Meta titles and H1 titles should, in most cases, match the title of the content. Meta descriptions should again advertise the subject of the content, hopefully intriguing the searcher to read more.
Where possible, keywords in your long tail content should be hyperlinked to the relevant of your main website. This is the topics approach that was referred to earlier - helping pillar pages to rank more highly for competitive terms by strategically forming clusters of related content.
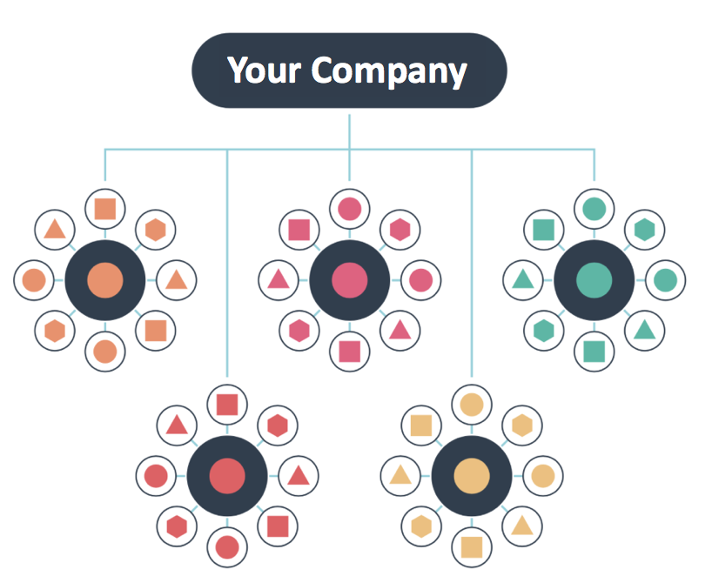
Source: HubSpot
Step 5 - Monitor and improve
Taking these steps ensures that you have a website designed for SEO and it's in good shape to rank well for your target keywords and topics almost immediately. And, if you continue to follow a content marketing strategy, you should be able to improve rankings over time.
Whatever your current situation, monitoring your SEO performance provides valuable data for continuous improvement. Make sure you have a tool in place which can monitor your position against important keywords, so that you are able to research new opportunities and make changes to your strategy.